In this article, we will see what is Bluetooth, how it evolved, how it works and the latest version and applications of the same.
How the Name “Bluetooth” Derived?
Bluetooth wireless technology was named after a Danish Viking and King, Harald Blatand. His last name means “Bluetooth” in English. He is credited with uniting Denmark and Norway, just as Bluetooth wireless technology is credited with uniting two disparate devices.
Who Invented Bluetooth?
The Bluetooth technology emerged from the task undertaken by Ericsson Mobile Communications in 1994 to find an alternative to the use of cables for communication between mobile phones and other devices. Invented by Dutch electrical engineer Jaap Haartsen, working for telecommunications company Ericsson. In 1998, the companies Ericsson, IBM, Nokia, and Toshiba formed the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) which published the 1st version in 1999.
How does Bluetooth Technology work?
Bluetooth networking transmits data via low-power radio waves. It communicates on a frequency of 2.45 gigahertz (actually between 2.402 GHz and 2.480 GHz, to be exact).
It is a specification (IEEE 802.15.1) for the use of low power radio communications to link phones, computers and other network devices over short distances without wires. Wireless signals transmitted with Bluetooth cover short distances, typically up to 30 feet (10 meters).
What is the device used for Bluetooth transfers?
It is achieved by embedded low-cost transceivers into the devices. It supports the frequency band of 2.45GHz and can support up to 721KBps along with three voice channels. This frequency band has been set aside by international agreement for the use of industrial, scientific and medical devices (ISM), compatible with 1.0 devices.
Technical Definition
Technically, the wireless connection between two Bluetooth devices is known as a short-range, frequency hopping, ad hoc radio link. Bluetooth devices are managed using an RF topology known as a “star topology.” Under this topology, you can have one master and up to seven active slaves. The master is responsible for providing synchronization to all the slaves. This is known as a piconet.
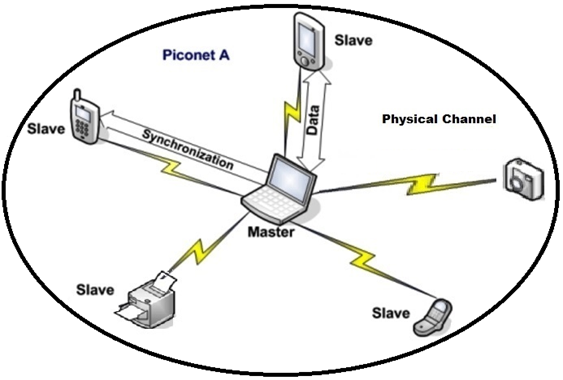
Any given device can be part of one or more piconets, as either a master or a slave. This is what makes Bluetooth technology so powerful.

How is Connection establishing between devices using Bluetooth?
Bluetooth Network consists of a Personal Area Network or a piconet which contains a minimum of 2 to a maximum of 8 Bluetooth peer devices simultaneously and each device offers a unique 48-bit address from the IEEE 802 standard with the connections being made a point to point or multipoint.
Usually a single master and up to 7 slaves. A master is a device that initiates communication with other devices. The master device governs the communications link and traffic between itself and the slave devices associated with it. A slave device is a device that responds to the master device. Slave devices are required to synchronize their transmit/receive timing with that of the masters. In addition, transmissions by slave devices are governed by the master device (i.e., the master device dictates when a slave device may transmit). Specifically, a slave may only begin its transmissions in a time slot immediately following the time slot in which it was addressed by the master, or in a time slot explicitly reserved for use by the slave device.
The frequency hopping sequence is defined by the Bluetooth device address (BD_ADDR) of the master device. The master device first sends a radio signal asking for a response from the particular slave devices within the range of addresses. The slaves respond and synchronize their hop frequency as well as a clock with that of the master device.
Scatternets are created when a device becomes an active member of more than one piconet. Essentially, the adjoining device shares its time slots among the different piconets.
Bluetooth can connect up to “eight devices”
Bluetooth Versions
The first version was 1.2 standard with a data rate speed of 1Mbps. The second version was 2.0+EDR with a data rate speed of 3Mbps. The third was 3.0+HS with a speed of 24 Mbps.
Bluetooth 4.0 has the high-speed capability of Bluetooth 3.0 but also comes with a Low Energy feature to collect data from the sensors of low rate devices. This feature allows the Bluetooth module to reduce power consumption with connected devices like wearable smartwatches, heart monitors, mobile phones and smart headphones.
The most recent version of the Bluetooth protocol, Bluetooth 5, is an improvement upon the previous BLE standards. It is still geared towards low powered applications but improves upon BLE’s data rate and range. Unlike version 4.0, Bluetooth 5 offers four different data rates to accommodate a variety of transmission ranges: 2Mbps, 1Mbps, 500kbps, 125kbps. Because an increase in transmission range requires a reduction in data rate, the lower data rate of 125kbps was added to support applications that benefit more from improved range. So reducing the data rate allows these sensors to transfer the information as far as 240 meters. The flexibility in data speeds offered by Bluetooth 5 allows low powered products to send even more sophisticated data to the end-user.
Bluetooth Applications
Cordless Desktop: Most of the peripheral devices (e.g., mouse, keyboard, printer, speakers, etc.) are connected to the PC cordlessly.
Ultimate headset: It can be used to allow one headset to be used with myriad devices, including telephones, portable computers, stereos, Home theaters, etc.
Multimedia Transfer: Exchanging of multimedia data like songs, videos, pictures can be transferred among devices using Bluetooth.
